Customizing Controllers and Broadcasters
The default GPIO configuration
The current GPIO controller comes with a set of GPIOs enabled by default. These configurations can be found in example_gpio_config.yaml
This config file contains four main sections,
io_stateshows current value/state of all sub-listed IO typesio_cmdcommands that could be used to change/update any of sub-listed gpionum_reg_stateshows the current value/state of gpio statenum_reg_cmdcommands used to update the gpio registers
listed items under each of these sections can be modified/remove/added to update the configuration of GPIO controller.
upon inspecting part of the example_gpio_config.yaml we can see
gpio_topic_config:
io_state:
- type: DI
start: 101
length: 12
- type: DO
start: 101
length: 12
...
io_cmd:
- type: DO
start: 101
length: 12
Here, the DI IO type shows up both under io_state and io_cmd so user would
be able to read from and write into in high frequency!
IO types which are not listed in the config file would still be available under
/fanuc_gpio_controller/* topic to be read/written into through a service call.
Passing a Custom Config File
A separate gpio configuration file could also be passed during launch by appending
gpio_configuration:=/path/to/new/config/file to your default ros2 launch command
Using CLI to Monitor/Switch GPIO
Users can monitor or set an IO through command line interface using the provided GPIO services in ROS2
After launching your ros2 launch, the list of available services can be listed by
ros2 service list
The GPIO services are under topic /fanuc_gpio_controller/*
One can access type of the service msg with
ros2 service type /fanuc_gpio_controller/get_bool_io
#which would return
fanuc_msgs/srv/GetBoolIO
and the given message details could be viewed by
ros2 interface show fanuc_msgs/srv/GetBoolIO
which returns
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2025, FANUC America Corporation
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2025, FANUC CORPORATION
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Supported types:
# DI
# DO
# RI
# RO
# F
IOType io_type
#
string AI=AI
string AO=AO
string DI=DI
string DO=DO
string RI=RI
string RO=RO
string SI=SI
string SO=SO
string WI=WI
string WO=WO
string UI=UI
string UO=UO
string WSI=WSI
string WSO=WSO
string F=F
string M=M
string GI=GI
string GO=GO
string type
uint16 index
---
int32 result
bool value
from the message type we can observe that this service expects a string for a variable called io_type as well as an index and in response it returns the current value of the io_type at that index.
for example lets try to first read the current state of first index in DO type IO.
ros2 service call /fanuc_gpio_controller/get_bool_io fanuc_msgs/srv/GetBoolIO "{io_type: {type: 'DO'}, index: 1}"
which would respond with
waiting for service to become available...
requester: making request: fanuc_msgs.srv.GetBoolIO_Request(io_type=fanuc_msgs.msg.IOType(type='DO'), index=1)
response:
fanuc_msgs.srv.GetBoolIO_Response(result=0, value=False)
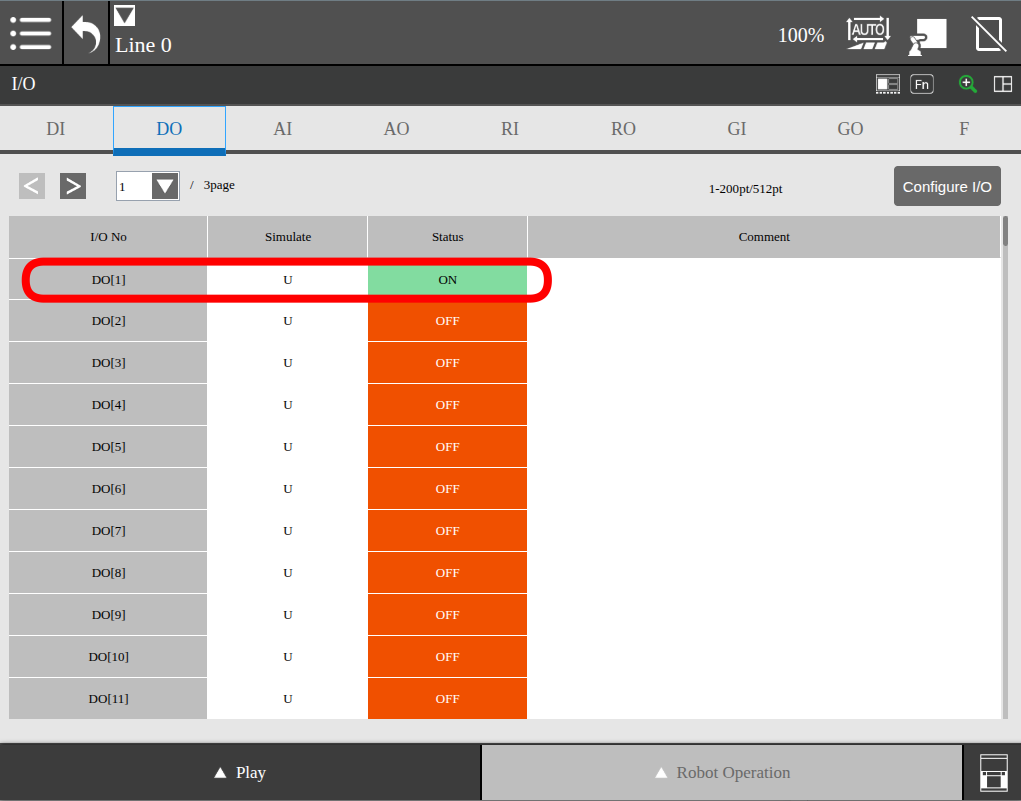
and the value=False
It is also visible on the pendant that this port is set to off.
this port could get switched on by calling
ros2 service call /fanuc_gpio_controller/set_bool_io fanuc_msgs/srv/SetBoolIO "{io_type: {type: 'DO'}, index: 1, value: true}"
which would respond by
waiting for service to become available...
requester: making request: fanuc_msgs.srv.SetBoolIO_Request(io_type=fanuc_msgs.msg.IOType(type='DO'), index=1, value=True)
response:
fanuc_msgs.srv.SetBoolIO_Response(result=0)
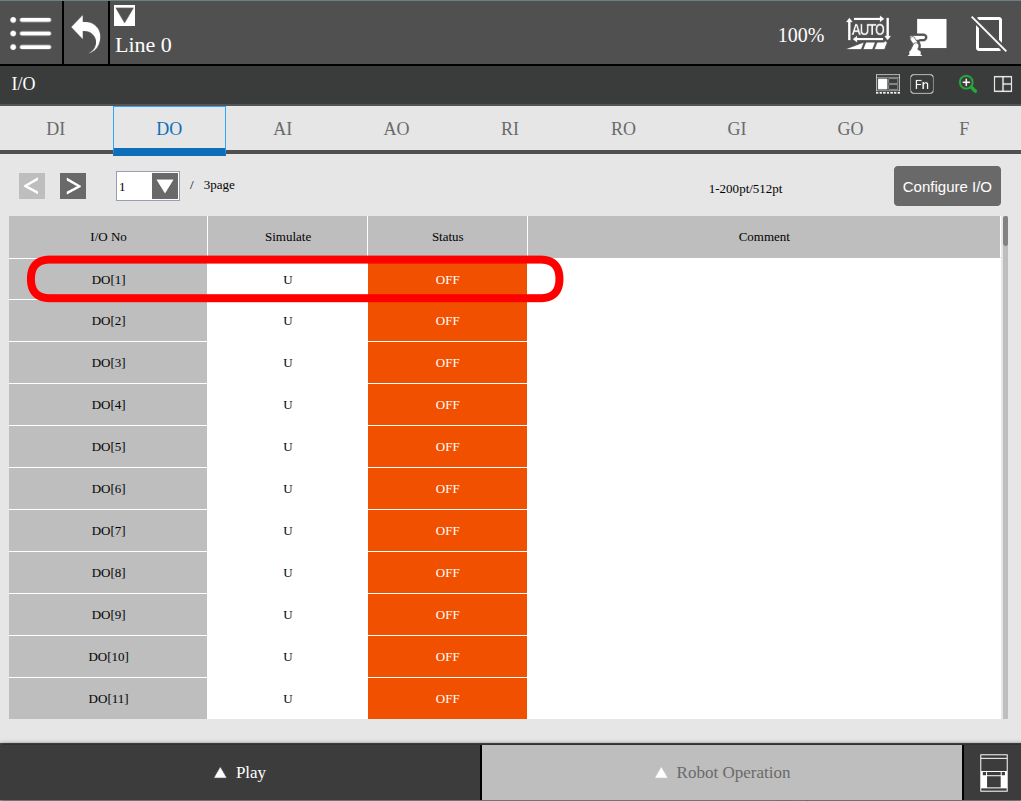
running the get_bool_io again to see the current state of the IO shows
waiting for service to become available...
requester: making request: fanuc_msgs.srv.GetBoolIO_Request(io_type=fanuc_msgs.msg.IOType(type='DO'), index=1)
response:
fanuc_msgs.srv.GetBoolIO_Response(result=0, value=True)
that value=True
this could also be verified on pendant