Troubleshooting
Common Issues
I cannot command motion and I received a RMI session timeout error
The controller will automatically terminate the connection when the client fails to send a command/instruction packet within the Remote Motion Interface (RMI) timeout (default is 60 minutes).
Once the connection is terminated, the client needs to be restarted.
You can change the default time by changing the system variable $rmi_cfg.$discnt_tim. Setting this variable to 0 disables the timeout check.
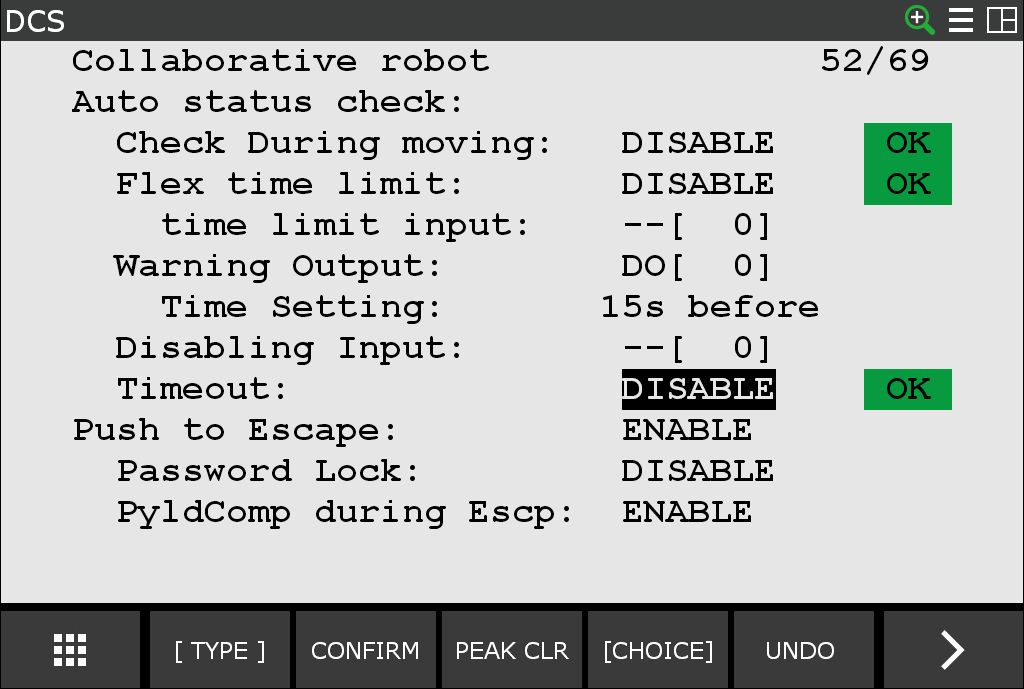
I cannot command motion and received a SYST-322 Auto Status Check timeout alarm
When the robot is keep moving for longer than the Auto Status Check timeout setting, a SYST-322 Auto status check time out alarm will be posted and the robot will stop.
This alarm can be suppressed in one of two ways: change the timeout value or disable the timeout. Both are safety features which require applying DCS changes and cycling power.
The following shows the screen for the Auto Status Check timeout.
I cannot command motion after accessing the teach pendant or E-stop
When running external motion commands through the ROS 2 controller interface, the external motion will stop as soon as there is a servo fault on the controller, triggered by such things as turning on the teach pendant or performing an E-stop. Afterwards, the ROS driver will not be able to send commands to the robot again until the controller’s fault is cleared and the ROS driver’s program has been restarted.
I get occasional robot motion faults
This may be attributed to your PC’s high CPU load; try the following suggestions to help alleviate the high CPU load:
Computers with high CPU loading may miss their command send windows, causing the robot to fault. You might need to adjust your real-time process priorities to ensure the timing of all command send windows or limit the number of concurrent tasks.
The Ubuntu PC should have the real-time kernel enabled.